| DE | EN | Contact | About us | Terms of Business | Imprint | Privacy & Cookies | Help | Newsletter | Registration | Login | |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Home > News > Case Studies > Power Supplies > Using a DC/DC converter as a USB charger | |||||||||||
Using a DC/DC converter as a USB chargerSchukat electronic advises on charging with RECOM converters
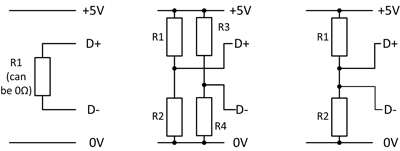
There is no universal USB charging solution on the market, a situation partly attributable to the variety of USB standards that exist. One practical option is offered by the various types of RECOM DC/DC converters, designed for a range of application areas.The problemThe well-known USB standards allow a maximum charging current of 500mA for USB 1.0 and 2.0 and 900mA for USB 3.0, with a fast-charging maximum current of 1.5A. Applying fixed voltages to the D+ and D- terminals or a resistor between these two data terminals determines the safely deliverable power of a charging device. In this way, a mobile device learns that it is connected to a Dedicated Charging Port (DCP). However, different manufacturers also use different specifications, which explains why there is no universal solution.
Attempted solutionsTo make this process easier, the USB 3.1 standard introduced a battery charging specification. The mobile device can thus communicate with the charger and – taking into account the charging capability of various mobile devices – determine variable limits for output voltage, amperage and power, and can also define the connection variant used: type A, type B, micro-B or type C.
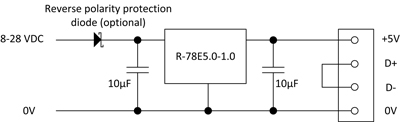
Thanks to backwards-compatible USB standards, mobile devices with a USB-C port can also be charged using an older charger. The only disadvantage: this charging process can take longer than using a dedicated USB 3.1 charger. Which DC/DC converters can be used as USB chargers?• For a cost-effective DCP solution — because mobile devices often accept a USB connector with shorted D- and D+ pins as DCP — a RECOM R-78E series buck converter can be used, for example. This solution is ideal for power supplies delivering 12 or 24VDC as well as for 12V lead-acid batteries.
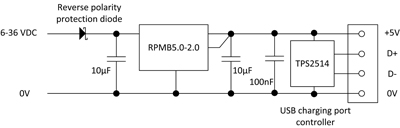
• When using a 24V lead-acid battery, RECOM’s pin-compatible R-78C5.0-1.0 will work, with an input voltage range of up to 42VDC. To protect against reverse polarity, having the diode connected in series is a prerequisite for battery-powered USB chargers.
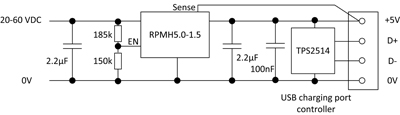
• If a higher input voltage range is called for, e.g. when using a 48V lithium-ion battery, a higher charging voltage is required. In this case, a converter that can handle input voltages of up to 60 VDC is needed, such as RECOM's RPMH5.0-1.5. This has a resistor divider between the input and enable pin to protect against undervoltage and turns off automatically if the input voltage drops below 20V, thus protecting the battery from deep discharge and possible damage.
• If an isolated charging connection is required — for example to avoid short circuits if the output pins should be connected to the power supply - RECOM’s RS6-4805S DC/DC converter can be used. Housed in a SIP8 miniature case, it delivers up to 1200mA. It also features a built-in undervoltage-lockout that can prevent battery damage from deep discharge, and 1.6kV DC/1 minute isolation that can withstand 100V voltage spikes, while a TVS diode provides ±1kV transient protection. The RS12 series delivers even higher power: up to 2.4A. At SchukatAt Schukat electronic we offer a range of different types of DC/DC converters from RECOM. Our technical sales team is also available to advise and support you on all aspects of power supply. |
|