| DE | EN | Contact | About us | Terms of Business | Imprint | Privacy & Cookies | Help | Newsletter | Registration | Login | |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Home > News > Case Studies > Power Supplies > Smart battery chargers: How chargers from MEAN WELL charge lithium and lead-acid batteries | |||||||||||
Smart battery chargers: How chargers from MEAN WELL charge lithium and lead-acid batteriesSchukat describes how chargers from MEAN WELL charge lithium and lead-acid batteries
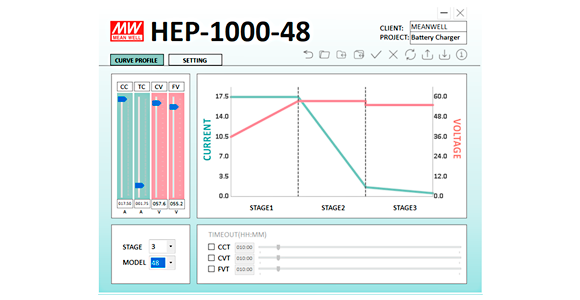
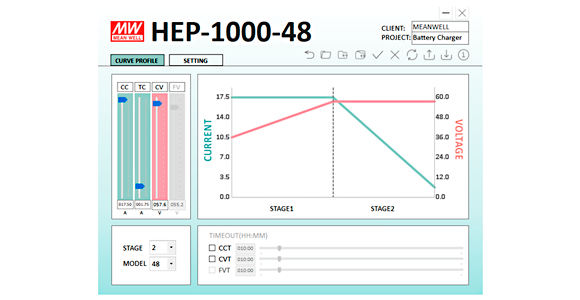
The two most commonly used battery types – lead-acid batteries and lithium batteries – differ in their characteristics and how they charge. Schukat electronic explains how a smart charger from MEAN WELL can be a real problem solver.As energy storage devices, batteries are used not only in consumer electronics, cars and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, but also in e-mobility and renewable energy storage. The varying characteristics of the different kinds of batteries, however, means it isn’t always easy to choose the right batteries or chargers. How do lead-acid batteries and lithium batteries differ?Lead-acid batteries offer higher charging voltage tolerance, high surge current capability, a broad operating temperature range, and low price. They are often used in drive applications – such as in cars or forklifts – or in emergency power systems. Their disadvantages, however, include high self-discharge and a relatively low number of charge/discharge cycles, which makes them unsuitable for energy storage applications. What is the best way to charge batteries?• Lead-acid batteries: Because of their high self-discharge, the 3-stage charging method is frequently recommended. A typical charging cycle begins with the constant-current stage – the charger limits its output current to the maximum rated current and slowly increases the output voltage. If the battery voltage has reached the maximum charging voltage, the charger switches over to the constant voltage stage. It then constantly outputs its maximum rated voltage and monitors its output current. Finally, when the charging current falls below about 10% of the rated current, the charger switches to the trickle-charge stage. In this stage, the charger reduces its output voltage to avoid overcharging the battery Smart battery chargersTo ensure the reliability, long service life, and safety of batteries, it is recommended to optimise the charging curve – in fact, this is mandatory for lithium batteries. MEAN WELL's programmable chargers with PMBus or optional CANBus interface, or the SBP-001 intelligent programmer, which includes free configuration software, all offer flexibility and a user-friendly interface for adjusting the charging curve. They are suitable for use with both lead-acid batteries and Li-ion batteries. Chargers in the HEP 1000 series from MEAN WELL• Standard setting: constant voltage 48V and max. 1008W (HEP-1000-48)
• Charging voltage and charging current for other kinds of lead-acid batteries adjustable to 36 to 60V and 3.5 to 17.5A respectively.
• Charging current can be reduced to prevent temperature increase, and voltage can be lowered to prevent possible overcharging. At SchukatAt Schukat electronic, we offer the smart battery chargers in MEAN WELL’s HEP-1000 series direct from stock. |
|